We all like fluffy white rice on our table. Have we ever thought why brown rice has a brown color and are different in taste? White rice is appealing to the customer as the white color, flavor, aroma and taste and texture appeals modern time consumers. The white rice is essentially brown rice polished several times after milling.
During polishing and refining, the brown color loses the brown color along with the nutrients, minerals, oils and vitamins contained in the husk. Polishing rice results in loss of 80%, and 67% of Vitamin B1 and B2, respectively. White rice contains 90% less of Vitamin B6, 50% less of manganese and phosphorus and almost 60 of iron. Almost all the fiber, an essential constituent of a diet is lost due to polishing.
Brown rice is the unpolished rice or more specifically hand polished rice. As it goes through less processing after the bran is removed, its color remains brown in addition to the retention of nutrients that are removed through polishing. As it contains the outer layer of bran and rice bran oil along with the embryo, it holds 100% of the nutrients contained in the bran layer. Therefore, it looks, smells and tastes different from white rice.
Why choose brown rice?
Rice is eaten by more than half the population of the world. It constitutes a major source of nutrients where it is the staple food. Brown rice is also known as “hulled” or “unmilled” rice. Unlike white polished rice it is light to deep brown in color. The fact that polishing the original brown rice removes most of its valuable nutrients required for growth and maintenance of human life have remained hidden in the society. Instead of the food and nutrient value that brown rice can add, the aesthetic white look of white rice is considered a way of marketing. Thus, brown rice is under-utilized even in the population where nutrient crisis exists. With knowledge on brown the choice of brown rice over white rice would be a logical one. Let’s look at some of the major benefits to health that brown rice—a nutrient dense cereal can provide us.
The Daily Value (DV %) of food requirement
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) calculate the Daily Value (DV) of food and determine the level of various nutrients in a normal serving of food to their approximate quantity needed relative to 2000 calories/day. According to the Food Rating System, a cup of brown rice has been calculated to contain a number of healthy essential nutrients with high DV. The understanding of the importance of the essential nutrients present in brown rice is essential for one to supplement the brown rice with white rice in their diet. The functioning of the most vital nutrients of brown rice will reveal the health benefits and improve in overcoming the vanity over white rice only.
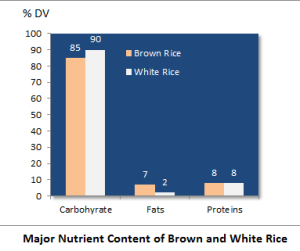
1.The calorie, carbohydrate, fat and protein of brown rice
A cup of brown rice weighs 195 g and provides 216 calories. This equates to 158 g of white rice providing 204 calories. Brown rice, therefore, provides carbohydrates of 85% of DV compared to 90% DV in case of white rice. Although the protein content is more or less the same in both brown and white rice the fat is much higher in brown rice. The higher calorie and fat availability of a cereal source should make brown rice more appealing to a large number of people who depend on rice as a basic food (Figure 1). Equally it is important for people who love rice, but would like to consume lower carbohydrate.
2.The fiber content of brown rice
Brown rice is known to contain a significantly higher fiber than white rice. The DV for carbohydrate is 14% compared to white rice of 7%. Dietary fibers, although not nutrients are desired as it reduces constipation and the formation of gas. Fiber in a diet is preferred as it regulates the bowel and helps in digestion. The main functions of dietary fiber are in smooth bowel functioning, lowering blood sugar levels and decreasing of cholesterol. Brown rice is good for patients having diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. Rice bran along with oat bran lower the total and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) which harms the active function of the heart. Due to the lower glycemic rating of brown rice it is known to control diabetes
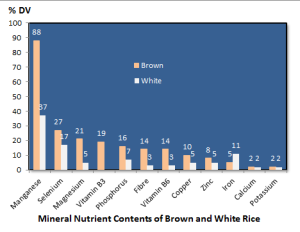
3.The nutrient dense nature of brown rice
Brown rice compared to white rice contains a higher percent DV of a number of minerals and nutrients (Figure 2). The DV values of minerals such as manganese, selenium, magnesium, phosphorus, copper and zinc are significantly higher in brown rice. The B Vitamins such as B6 and B3 supply 14 and 19% of DV of a human diet. This is because the outer layer of the rice grain contains an aleurone layer which is rich in Vitamin B. Brown rice usually preserve the embyro as they undergo less polishing. The aleurone layer and the endosperm together contain protein bodies not found in white rice.
4.The function of Manganese
Manganese activates a lot of enzymes. These enzymes, in turn aid in the metabolism of amino acids, especially glutamine the life of protein molecules. The enzymatic activities are tied to carbohydrate, vitamin B and Vitamin E in addition to cholesterol or fat cell production. As an important element of metabolism, manganese relieves a number of health conditions. A very remarkable influence of manganese is the premenstrual syndrome (PMS) that causes women to be irritated, go into mood swings, are depressed and have headaches during monthly periods. Manganese supplements relieve this condition and could very well be controlled by brown rice as it supplies 88% of the Daily Value.
Manganese is a constituent of thyroxine. Thyroxine regulates thyroid gland functioning and it is absolutely necessary to know that thyroid secretes hormones that control appetite, body weight and functioning of the reproductive system. Manganese also regulates the glucose absorption, thereby alleviating the diabetic condition. As it aids in vitamin absorption, it balances the utilization of other minerals in the body. It is one of the helpful elements for maintaining the digestive system, the nervous syatem, brain functioning and bone formation. The high functional performance of manganese is attributed to the prevention of cell damage formed by free radicals. It is an active antioxidant and the presence of manganese in brown rice makes it a wonderful nutrient dense cereal.
5.Selenium in brown rice
The importance of selenium in fighting against cancer, arthritis and heart diseases is well known. Having 10% more than white rice, this micronutrient works wonders and is rare in many food products. Selenium being a strong antioxidant protects cell damage. It relieves arthritis, reduces the risk of prostate cancer and improves fertility.
6.Phosphorus in brown rice
Rice bran is known to contain the highest amount of phosphorus and that is when rice is not polished. A cup of cooked rice has 162g Phosphorus, providing 17% of daily requirement. People with kidney problem, accumulate high phosphorus, a regulated amount is recommended for patients having dialysis.
7.Iron, copper and zinc
Although minor element, iron, copper and zinc is a component of blood. These minerals play vital role in metabolic functions. All nutrients combined brown rice is a nutrient dense cereal.
Brown Rice—a Healthy Cereal
Brown rice is healthier for us than white. With a changed mindset that having healthy food is being happy you can easily add brown rice to your diet. Of course, added with it a medium sized sea fish and salad makes it a balanced meal. You will be contented as it is low in carbohydrate, high in fat and the same amount of protein than white rice and significantly higher fat in brown rice. Above all brown rice is a nutrient dense cereal!







No Comments